This week, NASA's Planetary Science Division (PSD) hosted a community workshop at their headquarters in Washington, DC. Known as the "Planetary Science Vision 2050 Workshop", this event ran from February 27th to March 1st, and saw scientists and researchers from all over the world descend on the capitol to attend panel discussions, presentations, and talks about the future of space exploration.
One of the more intriguing presentations took place on Wednesday, March 1st, where the exploration of Mars by human astronauts was discussed. In the course of the talk, which was titled "A Future Mars Environment for Science and Exploration", Director Jim Green discussed how deploying a magnetic shield could enhance Mars' atmosphere and facilitate crewed missions there in the future.
The current scientific consensus is that, like Earth, Mars once had a magnetic field that protected its atmosphere. Roughly 4.2 billion years ago, this planet's magnetic field suddenly disappeared, which caused Mars' atmosphere to slowly be lost to space. Over the course of the next 500 million years, Mars went from being a warmer, wetter environment to the cold, uninhabitable place we know today.

Artist's rendering of a solar storm hitting Mars and stripping ions from the planet's upper atmosphere. Credits: NASA/GSFC
This theory has been confirmed in recent years by orbiters like the ESA's Mars Express and NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN Mission (MAVEN), which have been studying the Martian atmosphere since 2004 and 2014, respectively. In addition to determining that solar wind was responsible for depleting Mars' atmosphere, these probes have also been measuring the rate at which it is still being lost today.
Without this atmosphere, Mars will continue to be a cold, dry place where life cannot flourish. In addition to that, future crewed mission - which NASA hopes to mount by the 2030s - will also have to deal with some severe hazards. Foremost among these will be exposure to radiation and the danger of asphyxiation, which will pose an even greater danger to colonists (should any attempts at colonization be made).
In answer to this challenge, Dr. Jim Green - the Director of NASA's Planetary Science Division - and a panel of researchers presented an ambitious idea. In essence, they suggested that by positioning a magnetic dipole shield at the Mars L1 Lagrange Point, an artificial magnetosphere could be formed that would encompass the entire planet, thus shielding it from solar wind and radiation.
Naturally, Green and his colleagues acknowledged that the idea might sounds a bit "fanciful". However, they were quick to emphasize how new research into miniature magnetospheres (for the sake of protecting crews and spacecraft) supports this concept:
"This new research is coming about due to the application of full plasma physics codes and laboratory experiments. In the future it is quite possible that an inflatable structure(s) can generate a magnetic dipole field at a level of perhaps 1 or 2 Tesla (or 10,000 to 20,000 Gauss) as an active shield against the solar wind."
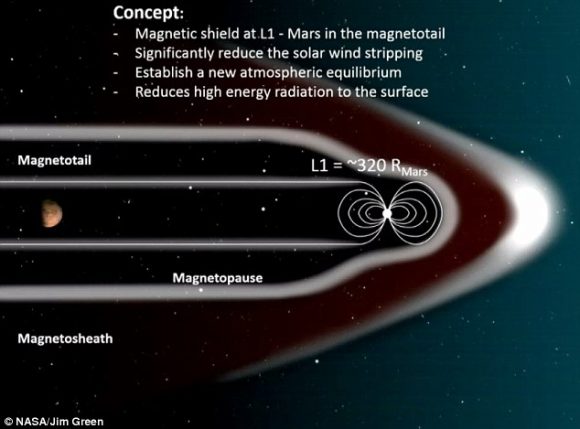
The proposed method for creating an artificial magnetic dipole at Mars' L1 Lagrange Point. Credit: NASA/J.Green
In addition, the positioning of this magnetic shield would ensure that the two regions where most of Mars' atmosphere is lost would be shielded. In the course of the presentation, Green and the panel indicated that these the major escape channels are located, "over the northern polar cap involving higher energy ionospheric material, and 2) in the equatorial zone involving a seasonal low energy component with as much as 0.1 kg/s escape of oxygen ions."
To test this idea, the research team - which included scientists from Ames Research Center, the Goddard Space Flight Center, the University of Colorado, Princeton University, and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory - conducted a series of simulations using their proposed artificial magnetosphere. These were run at the Coordinated Community Modeling Center (CCMC), which specializes in space weather research, to see what the net effect would be.
What they found was that a dipole field positioned at Mars L1 Lagrange Point would be able to counteract solar wind, such that Mars' atmosphere would achieve a new balance. At present, atmospheric loss on Mars is balanced to some degree by volcanic outpassing from Mars interior and crust. This contributes to a surface atmosphere that is about 6 mbar in air pressure (less than 1% that at sea level on Earth).
As a result, Mars atmosphere would naturally thicken over time, which lead to many new possibilities for human exploration and colonization. According to Green and his colleagues, these would include an average increase of about 4 °C (~7 °F), which would be enough to melt the carbon dioxide ice in the northern polar ice cap. This would trigger a greenhouse effect, warming the atmosphere further and causing the water ice in the polar caps to melt.

Artist's impression of the terraforming of Mars, from its current state to a livable world. Credit: Daein Ballard
By their calculations, Green and his colleagues estimated that this could lead to 1/7th of Mars' oceans - the ones that covered it billions of years ago - to be restored. If this is beginning to sound a bit like a lecture on how to terraform Mars, it is probably because these same ideas have been raised by people who advocating that very thing. But in the meantime, these changes would facilitate human exploration between now and mid-century.
"A greatly enhanced Martian atmosphere, in both pressure and temperature, that would be enough to allow significant surface liquid water would also have a number of benefits for science and human exploration in the 2040s and beyond," said Green. "Much like Earth, an enhanced atmosphere would: allow larger landed mass of equipment to the surface, shield against most cosmic and solar particle radiation, extend the ability for oxygen extraction, and provide "open air" greenhouses to exist for plant production, just to name a few."
These conditions, said Green and his colleagues, would also allow for human explorers to study the planet in much greater detail. It would also help them to determine the habitability of the planet, since many of the signs that pointed towards it being habitable in the past (i.e. liquid water) would slowly seep back into the landscape. And if this could be achieved within the space of few decades, it would certainly help pave the way for colonization.
In the meantime, Green and his colleagues plan to review the results of these simulations so they can produce a more accurate assessment of how long these projected changes would take. It also might not hurt to conduct some cost-assessments of this magnetic shield. While it might seem like something out of science fiction, it doesn't hurt to crunch the numbers!
Stay tuned for more stories from the Planetary Science Vision 2050 Workshop!
Further Reading: USRA



















